According to the James Consulting, Fujitsu Laboratories announced today that they have successfully developed a portable breathing sensor that can accurately and quickly measure the concentration of specific gas components, such as the low-level component of human exhaled gases, ammonia, in human breathing. The ammonia content is thought to be associated with certain living diseases. Prior to this, some gas molecules could only be detected and identified by large analytical instruments. With the birth of this sensor, gas detection will be made simple.
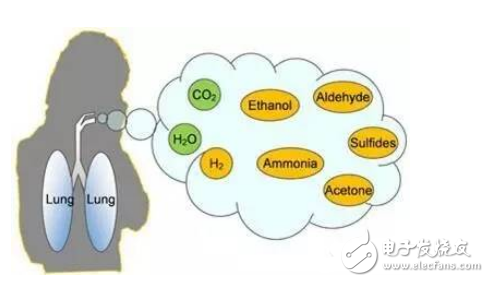
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of human respiratory exhaust gas composition
In view of the association between ammonia exhaled by human breath and liver metabolism and Helicobacter pylori infection (risk factors for gastric cancer), Fujitsu Laboratories developed a sensor capable of detecting trace amounts of ammonia using the ammonia adsorption characteristics of cuprous bromide for detection. The human exhaled ammonia content in the gas, this sensor is about 2500 times more sensitive to ammonia than other gases.
About this technology
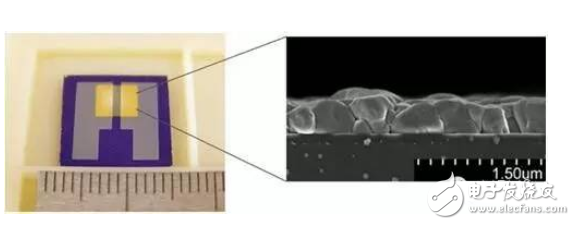
Figure 2 Photograph of the new sensor and cross-section electron scanning micrograph of cuprous bromide film
Copper bromide contains monovalent copper ions, which is a P-type semiconductor that can reversibly adsorb ammonia molecules. Using this property, Fujitsu Laboratories developed a respiratory gas sensor that optimizes the film thickness and cuprous bromide deposit in the sensor. The power supply effect of the ammonia molecules reduces the carriers in the sensor film, resulting in an increase in resistance between the electrodes. This phenomenon can be used to judge the occurrence of the reaction between ammonia gas and cuprous bromide. Therefore, the sensitivity of the sensor to ammonia is 2,500 times that of acetone, which is also a common component in human exhaled gases. The sensor's sensitivity to ammonia identification and concentration measurement is 10 ppb (parts per billion).
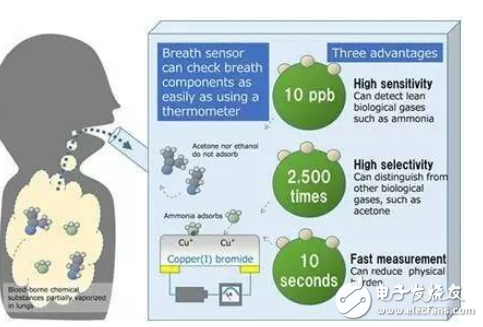
Figure 3 The working principle and advantages of the newly developed breathing sensor
Future plan
Fujitsu Laboratories plans to continue its in-depth study of the technology, increase the types of gases that can be monitored, and embed sensors into smart devices and wearable devices to make breathing gas detection as simple as using a thermometer.
Moving Walk,Elevator Escalator,Automatic Travelator,Automatic Escalator System
XI'AN TYPICAL ELEVATOR CO., LTD , https://www.chinaxiantypical.com